With the advent of computers and then their subsequent infiltration into every aspect of our lives, with the latest being the ease with which many terabytes of data/information can be stored & accessed remotely and communicated to the world within minutes. We are living in a world where our devices, appliances, & machines have the capability to be interconnected & operated through touch/voice.
This technology is about to invade & take over the gigantic & critical tasks in the world. The dawn of the computer age & the ending of the Industrial Revolution was much hyped by the media during the 1990s, but as we can observe, this revolution has entered a new stage with computers playing an active part in the industry of the future.
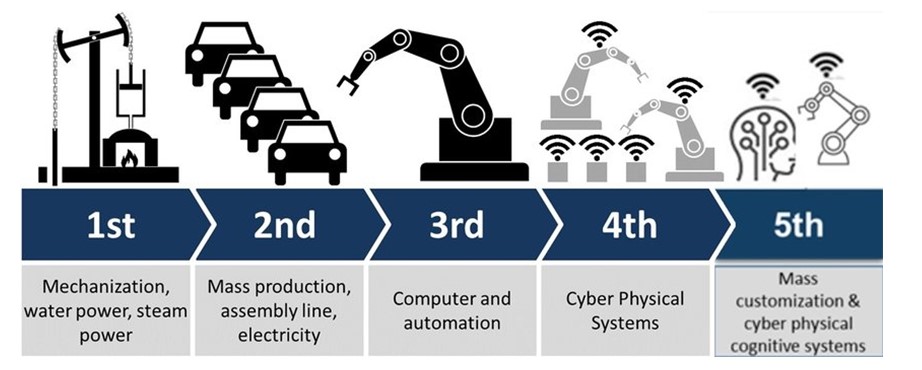
The term ‘Industry 4.0 was first coined & used by BOSCH, in Germany at the Hannover Trade fair in 2011, and is prevalent in the contemporary manufacturing sector to denote the worldwide use of cyber physical systems. It is defined by the level of automation attained so that the machines can mostly do their own tasks by using IOT, cloud computing, & big data. Like the concept of ‘smart homes’ a network of smart factories will come up by using digital technologies like sensing, programming memory, facial & voice recognition, etc., i.e., Industry 4.0 will introduce the following into the manufacturing sector-
- Machines run by computers (the cyber physical system)
- Connected & related Mechanical devices, equipment, & vehicles that are embedded with computer sensing, scanning, & monitoring ability (basically IOT)
- Data accessibility, hosting, & back-up from anywhere (basically cloud computing)
- Technical platforms using AI (basically, cognitive computing).
Requirements of the Industry 4.0 factory/system
To fully use the potential of current technology, four basic needs must be met:
- All industrial equipment & vehicles should be integrated with a computer IoT network – also termed ‘interoperability’
- Sensor enabled computers systems that can create online copies of real-world machinery & objects.
- Equipping machines & equipment with AI to help the humans with better decision-making & physical labour.
- Enable computer systems to execute tasks on their own (may be understood as decentralized decision-making).
Industry 4.0 demonstrates how digital/cyber technology has pervaded into manufacturing & is enabled to that level that it accomplishes high-tech cognitive & intellectual task besides physical tasks. This can lead to the creation of self-sustaining factory networks that can efficiently run physical tasks & immediately correct any shortcomings without involving humans. As the IoT infrastructure of all factories will be related through cloud computing & AI so the production house can network globally.
Some hurdles in the way of implementing Industry 4.0 smoothly –
- Problems may arise in machine-to-machine communication & its reliability.
- Issues related to IT security
- The phobia of internet & IT discrepancies.
- Lack of adequate skills-set in the employees who need to implement this.
- The fear of losing jobs & increased unemployment
Seeing the present scenario, it can be observed that these cyber-physical systems are more robust than the orthodox manual systems at producing uniformly with meticulousness. Due to this, factories & systems would see a nullification of work-related injuries & deaths. More jobs would be directed towards the supervision & maintenance of these cyber/cyber-physical systems, so there would be a boom in the requirement of skilled workers. Effective implementation of Industry 4.0 would lead to better consistency in production by eliminating the factor of human error in production, which will ultimately result in building a quality reputation for the company & a loyal customer base due to intensive customization.
Essentials for implementing Industry 4.0 – involves the following –
CAD– computer-aided drafting
CAM– computer-aided manufacturing
ERP-enterprise resource planning
MES – manufacturing execution systems
PLM – product lifecycle management
The smooth adoption & implementation of Industry 4.0 could prove to be a game-changer for the newbies & quick adopters who can become leaders in the future.
Visionary leaders are now discussing Industry 5.0 that forecasts the re-emerging of human involvement in the industrial sector. Here human & machines will come together to work & enhance the ways & efficacy of production. Mankind is likely to undertake lighter & creative work/tasks while the machines are involved in more laborious tasks. It is predicted that Industry 5.0 will amalgamate the intelligence of human & the cognitive computing ability of the new cyber systems to attain newer of speed & perfection in manufacturing. Industry 5.0 would also prove to be more meritorious for our environment as companies will be more directed towards sustainable development. As AI & Robots improve and become more like human, the interaction between man, machines, & computers will be more purposeful & mutually insightful that would make for a better working environment.
We know that the first three industrial revolutions took decades to unfold, but in the contemporary world, these will remain only till industry-wide implementation happens. That is why discussions about Industry 5.0 are following Industry 4.0. In the years to come, human & robots may start cooperating on designing & sharing workloads across different manufacturing processes. The term industry 5.0 has been doing the rounds since 2017 but formally gained significance in 2021 when the European Commission called for the fifth Industrial Revolution after two virtual workshops were organized by Directorate-General for Research & Innovation, on 2nd & 9th July 2020 & released a document titled ‘Industry 5.0: Towards a Sustainable, Human-centric, & Resilient European Industry’ on 4th Jan’ 2021.
While the major consideration of Industry 4.0 is technology, Industry 5.0 is driven by our values as it aims to use the potential of the industry towards the progress of society beyond jobs & growth by providing prosperity, balancing production in such a way that respects our planet, while maintaining the well-being of the workers involved. Industry 5.0 focuses on the significance of innovation & research in such a way that industry serves humanity while maintaining natural balance.
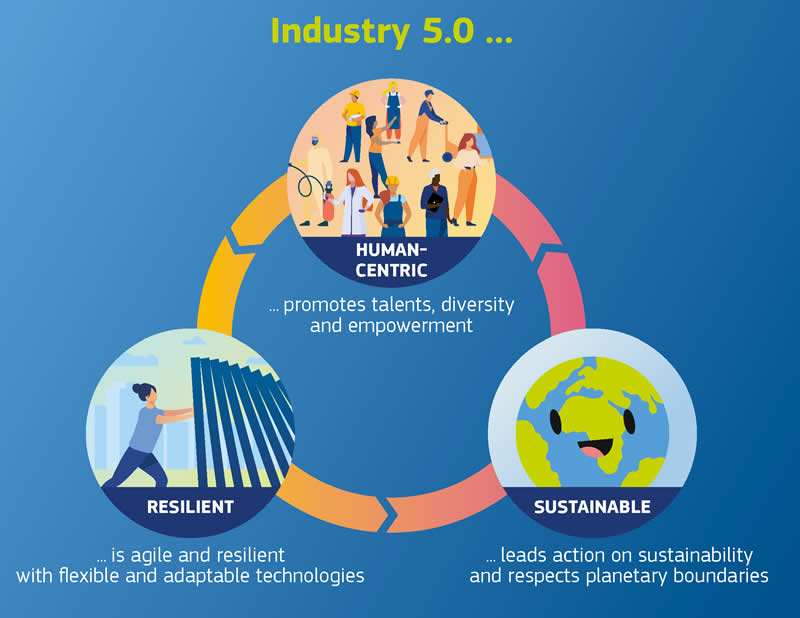
Industry 5.0 can complement Industry 4.0 by helping it transition to a more, sustainable, humanistic, and resilient industry, as the concept of Industry 5.0 has been created for supporting the values that society will/may have in the future.
The humanistic approach would mean the creation & use of technology to serve the society while making it adaptive to the needs & diversity of the workers. The workers would need to follow the concept of CURE (C-cross-skilling, U-upskilling, R-reskilling & E-expert skilling) to stay relevant for the industry. Sustainability would mean a cyclic process that gives back to nature what it takes from it. Resilience would mean the ability of a system to handle crises & disruptions & even natural emergencies.
While Industry 4.0 connected systems, processes, & machines for optimal performance, Industry 5.0 refines the collaborative interactions between human & machines to take efficiency and productivity to the next level.

Author:
Mr. Komal Mehrotra
Assoc. Prof. Communication & Soft Skills
HOD – Humanities & Social Sciences
KIET Group of Institutions
